Universal transmission device is used to transfer power between two shafts whose relative position changes continuously during the working process. Its function is to connect the transmission output shaft and the main reducer input shaft not in the same straight line, and ensure that the Angle and distance between the two shafts often change, still can reliably transfer power.
It is mainly composed of universal joint, drive shaft and middle support. The universal joint forks at both ends of the drive shaft must be in the same plane when installed.
First, the working principle
Universal joint, namely universal joint, is to achieve variable Angle power transmission parts, used for the position of the need to change the direction of the transmission axis, it is the "joint" part of the universal transmission device of the automobile drive system. The combination of universal joint and drive shaft is called universal joint transmission device. Universal transmission device is generally composed of universal joint and drive shaft, and sometimes there is a middle support, mainly used for the following positions: 1- universal joint; 2- drive shaft; 3- Front drive shaft; 4- Intermediate support. In a universal joint fit, the rotation of one part (output shaft) about its own axis is driven by the rotation of another part (input shaft) about its axis.
According to whether the universal joint has obvious elasticity in the torsion direction, it can be divided into rigid universal joint and flexible universal joint. The rigid universal joint can be divided into unequal universal joint (commonly used for cross shaft type), quasi-constant speed universal joint (such as double universal joint) and constant speed universal joint (such as ball cage universal joint) three kinds.

1. Non-uniform universal joint
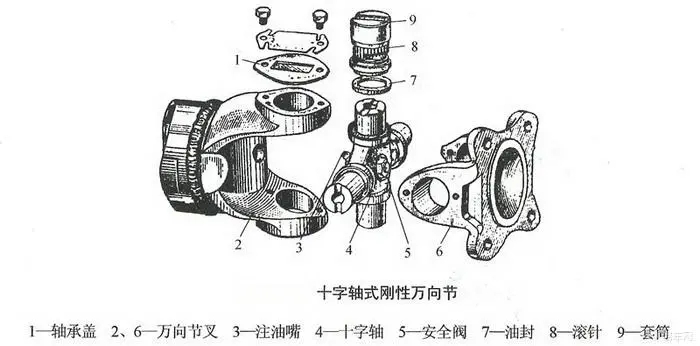
When the Angle between the two axes connected by the universal joint is greater than zero, the universal joint with the same average angular velocity moves between the output axis and the input axis at varying instantaneous angular velocity ratio. The cross shaft type rigid universal joint is composed of universal joint fork, cross shaft, needle roller bearing, oil seal, sleeve, bearing cover and other parts.
The working principle is: one of the rotating forks drives the other fork to rotate through the cross shaft, and at the same time can swing around the center of the cross shaft in any direction. The needle roller in the needle roller bearing can rotate during rotation to reduce friction. The shaft connected with the input power is called the input shaft (also known as the active shaft), and the shaft output by the universal joint is called the output shaft (also known as the driven shaft). Working under the condition that there is an included Angle between the input and output shafts, the angular velocity of the two shafts is not equal, which will lead to torsional vibration of the output shaft and the transmission parts connected with it and affect the life of these parts.
2. Quasi-constant velocity universal joint
A universal joint that transmits motion at the same instantaneous angular velocity at the designed Angle and at approximately the same instantaneous angular velocity at other angles. It is divided into:
A. Double quasi-constant velocity universal joint. Refers to the universal joint where the length of the drive shaft in the constant speed transmission device of the universal joint is reduced to the minimum.
B. Convex block quasi-constant velocity universal joint. It consists of two universal joints and two convex blocks of different shapes. The two convex blocks are equivalent to the middle drive shaft and two cross pins in the double universal joint device.
C. Three-pin quasi-constant velocity universal joint. It consists of two three-pin shafts, active eccentric shaft forks and driven eccentric shaft forks.
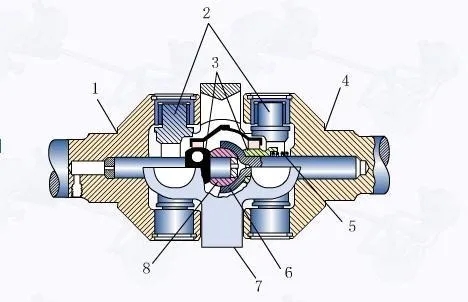
D. Spherical roller quasi-constant velocity universal joint. It consists of a pin shaft, a spherical roller, a universal joint shaft and a cylinder. Roller can do axial movement in the groove, play the role of expansion spline. Roller contact with groove wall can transfer torque.
3. Constant velocity universal joint
The output axis and the input axis connected by the universal joint transmit the moving universal joint at always equal instantaneous angular velocity. It is divided into:
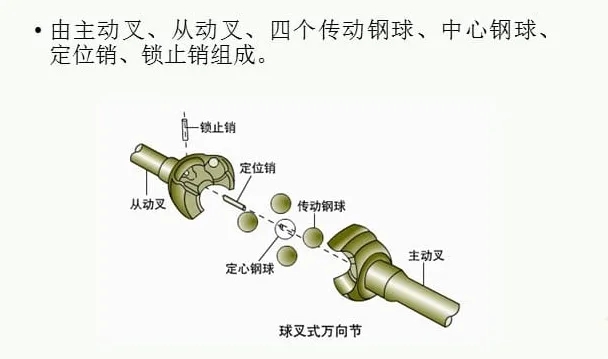
A. Ball fork constant velocity universal joint. A universal joint consisting of a ball fork with a raceway and a steel ball. And the circular groove raceway ball fork universal joint refers to the ball fork on the ball raceway for the circular arc universal joint. The structure is characterized by an arc groove on the active fork and the driven fork of the ball fork, which forms four ball raceway after assembling, and a total of four balls are accommodated in the raceway. The centering steel ball is arranged in the spherical groove in the center of the main and driven forks. Straight groove raceway type ball fork universal joint refers to the steel ball raceway on the ball fork is straight groove raceway type universal joint. Its structure is characterized by a straight groove made on two ball forks, each straight groove and the axis of the center line phase tilt, and the tilt Angle is the same and symmetric each other. Four steel balls are arranged in the raceway between the two ball forks.
B. Ball cage constant velocity universal joint. According to whether the universal joint can move in the axial direction, it can be divided into axial non-telescopic (fixed) ball cage universal joint and telescopic ball cage universal joint. Structure fixed type ball cage universal joint star sleeve inside the inner surface spline and drive shaft connection, its outer surface system has 6 arc groove as the inner raceway of the steel ball, the outer raceway is done on the inner surface of the spherical shell. After assembling the star sleeve and spherical shell, there are 1 steel balls in each of the 6 raceways, and the 6 steel balls are in the same plane by the cage (ball cage). The power is transferred from the drive shaft through the steel ball and spherical shell (Figure 2). The structure of the telescopic ball cage universal joint is characterized by a cylindrical straight groove on the inner wall of the cylindrical shell and the external of the star sleeve, and a steel ball is installed in the raceway formed after the two are assembled. The balls are also mounted in the holes of the cage. The inner hole of the star sleeve is splined to connect with the input shaft. This structure allows the star sleeve to move in the axial direction relative to the cylindrical shell.


Mobile station

WeChat